Solar energy is created by nuclear fusion that takes place in the sun. The amount of sunlight that reaches the Earth's surface in an hour and a half is enough to manage the entire world's energy consumption for a whole year. solar technologies convert sunlight into electrical energy by means of photovoltaic (PV) panels or mirrors that concentrate solar radiation. This energy can be used to generate electricity or be stored in batteries or thermal storage.
Over the years, the United States has come a long way in positioning itself as a leader in solar energy production, along with China, India, Japan and Vietnam. Although solar energy was once seen as a niche market, these countries are demonstrating that this renewable energy source is a legitimate answer to the global search for alternatives to fossil fuels. The vast majority of photovoltaic products, or solar panels, are being installed in remote areas by giant solar farms that sell energy to utilities. Satellite images show the incredible growth of these huge solar farms that continue to appear all over China.
China's dramatic increase in solar power is due to the nation's desperate need for electricity and its severe air pollution crisis. While some countries have reduced incentives to install solar panels, China's government is strongly encouraging financial institutions to incentivize solar installations. The United States has continued to improve its position as a leader in solar energy by expanding its utility sector and its facilities in the residential market. Much of the increase is due to significant government incentives given to the residential sector, which is a fast-growing market segment.
The International Energy Agency estimates that solar energy production accounts for 700 million tons of CO2 savings each year. The photons that reach the solar cells and generate an electric current come from somewhere: the sun. Solar energy is created by the constant nuclear fusion reactions that occur deep in the sun. Nuclear fusion in the sun occurs when protons (which are essentially the same as hydrogen atoms) collide and fuse at extreme temperatures and pressures to create helium.
This process emits a massive amount of energy (in addition to more protons), and in the center of the sun, this reaction occurs constantly, producing more than 500 million tons of hydrogen atoms per second. Renewable energy is now the lowest-cost source of energy generation, meaning that the more solar, wind and energy efficiency you choose instead of fossil fuels, the lower the utility bills will be for all. Securing funding for solar infrastructure in black and indigenous communities and communities of color can ensure that the benefits of solar energy are available to all. The material capacity of solar energy has the potential to empower communities by allowing them to own and generate their own energy.
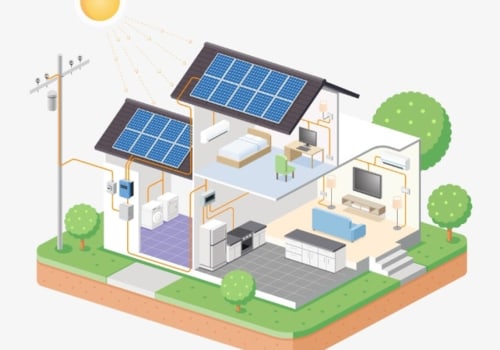
Within the cumulative photovoltaic capacity in the United States, there has been growth in the distributed generation segment, which are all grid-connected photovoltaic installations in residential and non-residential markets. Non-residential market includes facilities on commercial, government, school and non-profit properties. Photovoltaic panels on the roof of a house in Boston Photovoltaic panels in a city hall Photovoltaic panels in a school building Solar panels connected to poles in New Jersey An SREC program is an alternative to the popular power tariff model in Europe. The key difference between the two models is the market-based mechanism that drives the value of SRECs and, therefore, the value of the subsidy for solar energy.
In a power tariff model, the government sets the value of electricity produced by a solar installation. If the level is higher, more solar energy is built and the program is more expensive. If the power tariff is set lower, less solar energy is generated and the program is inefficient. The problem with SRECs is the lack of certainty for investors.
A feed fee provides a known return on investment, while an SREC program provides a potential return on investment. Although more can be done to harness the energy of that bright fireball in the sky, several countries have taken the lead in capturing energy from the sun and are using it as a viable source of electricity. Yes, solar energy is a renewable and infinite source of energy; as long as the sun is still shining, energy will be released. Over the same time period, total solar generation, including estimated small-scale photovoltaic generation, was 96.1 TWh, or 2.30% of total U.
When photons, or light particles, collide with the thin layer of silicon on top of a solar panel, they eject electrons from silicon atoms. The capacity factor of solar photovoltaic units is highly dependent on climate and latitude, so it varies significantly from state to state. Latitude, climate and weather patterns are important factors affecting insolation, the amount of solar radiation received on a given surface during a specific period of time. A solar energy tower uses a set of tracking reflectors (heliostats) to concentrate light on a central receiver on a tower.
As one of the most densely populated countries in the world, Japan cannot afford to cover huge tracts of land with solar panels. Solar farms, also known as solar parks or solar fields, are large areas of land that contain interconnected solar panels placed together on many acres, to collect large amounts of solar energy at the same time. Learn more about the groundbreaking research being conducted by the Office of Solar Energy Technologies in these areas. FIT is a policy that helped encourage the faster development and use of solar energy, making Germany and Italy the leaders in today's solar energy market.
In 1954, photovoltaic technology was born when Daryl Chapin, Calvin Fuller and Gerald Pearson developed the silicon photovoltaic cell at Bell Labs in 1954, the first solar cell capable of absorbing and converting enough solar energy into energy to run daily electrical equipment. Solar thermal energy is less sophisticated and simply the direct heating of water (or other fluids) by sunlight. This process is called the photovoltaic effect and is the fundamental chemical and physical process behind the vast majority of solar technology. The output power of the photovoltaic system also depends on the ambient temperature, wind speed, solar spectrum, local dirt conditions and other factors.
. .











Leave a Comment